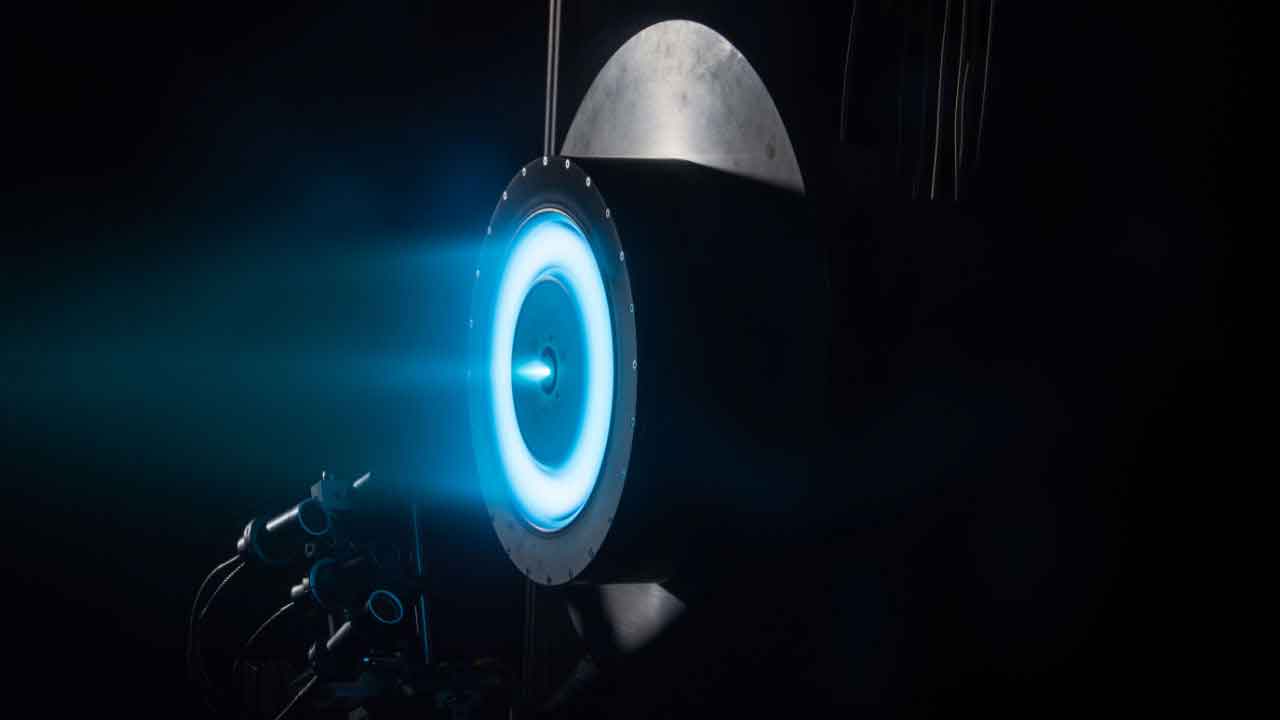
Hall Effect Thrusters and the Telecommunications Space Race
In the early 2000s as the internet started up the exponential growth curve, much consideration was given to constellations of satellites providing access to isolated areas of the Earth. Satellite communication companies like Irridium and Teledesic were highlighted in nearly every publication remotely related to space and the internet.
The prospect of so many satellites designed to fall out of their Low Earth Orbits on a regular basis fueled the interest in the development of Hall Effect/Ion Thrusters (HETs). Their designs and materials were constantly evolving in an effort to find the sweet spot between weight, propulsion and cost. Due to the extreme environments that satellites must endure, the discharge channels and cathode insulators used in HETs require a very demanding set of properties.
HET Material Requirements
- High dielectric strength – they must be very dielectric due the voltages involved
- Thermal shock resistant – satellites are exposed to extreme temperature fluctuations in space
- High thermal conductivity – thermally-generated electrical conditions require adequate cooling
- Low CTE – due to temperature fluctuations it is imperative that the HTC remain dimensionally stable
- Low density – the weight of space-bound components is critical for efficient launching and operation
The demanding conditions that HET must endure necessitate very precise and often complex designs that can only be economically created with machinable ceramics. Conventional ultra-hard ceramics require intensive manufacturing methods that often involve bespoke pressing, green machining, sintering, and costly diamond grinding.
Early HET Materials
Borosil was one of the earlier machinable ceramics developed to fit these diverse demands. At approximately 49% SiO2, 49% BN, 1% Y2O3, Borosil came from Russia at Kaliningrad. While adequate for HET applications, many in the satellite community needed a material with Western availability. Saint-Gobain (previously the Carborundum Company of Niagara Falls, New York) had suitable materials on the shelf.
Boron Nitride Discharge Channels and Cathode Insulators
Saint-Gobain’s M26 grade of hexagonal boron nitride was the first material to evolve as a replacement for Borosil. M26 is a unique composite of 60% proprietary BN crystals, and 40% semiconductor-grade SiO2. It has consistently met or exceeded the requirements of dielectric strength, thermal shock resistance, refractoriness, machinability and secondary-ion erosion resistance. Many designs have been launched with M26 HET discharge channels and cathode insulators.
Saint-Gobain has continued to develop materials for severe requirements. Their HP grade, with approximately 95% BN with a calcium-borate binder, has survived extensive design and testing. It continues to be evaluated by the major thruster designers, along with the work by many colleges and universities. In this arcane field, HP is considered an “accepted” and proven grade of boron nitride.
And finally, there is work underway using Saint-Gobain’s AX05 Grade. The highest-purity hBN on the market, AX05 also meets the above list of requirements, along with a unique softness relative to the other BN grades. This softness plays an interesting role in the very esoteric arena of secondary-ion emission. While relatively new to the application, AX05 has been a key Saint-Gobain grade for over 20 years.
Only now is there a more serious effort going into satellite constellations for universal internet connectivity. The use of Boron Nitride in discharge channels and cathode insulators is integral to the success of Hall Effect Thrusters.
China Ceramic Parts is your hBN Expert
All these Boron Nitride Grades, plus many other ceramic materials are available in bulk, or as machined components. China Ceramic Parts has many years of experience working with aerospace applications and has the latest machining and measuring equipment to make incredibly intricate and high tolerance parts.
This post was written by Steve Lyle. Steve has a BS in Ceramic Science from Penn State and over 35 years of experience working with BN products at Carborundum/Saint Gobain.